Aligning individual brains with Fused Unbalanced Gromov-Wasserstein
Abstract
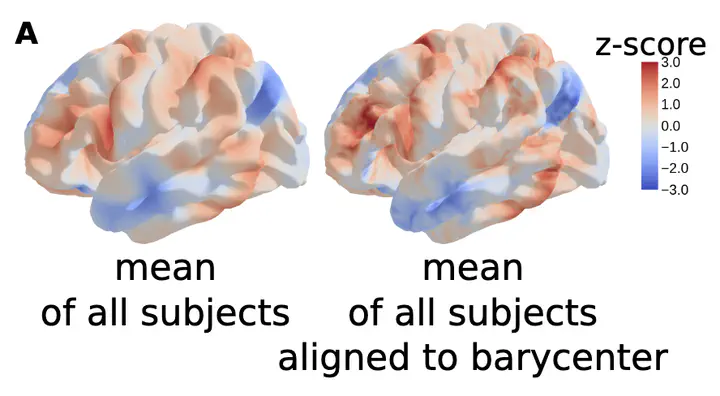
Individual brains vary in both anatomy and functional organization, even within a given species. Inter-individual variability is a major impediment when trying to draw generalizable conclusions from neuroimaging data collected on groups of subjects. Current co-registration procedures rely on limited data, and thus lead to very coarse inter-subject alignments. In this work, we present a novel method for inter-subject alignment based on Optimal Transport, denoted as Fused Unbalanced Gromov Wasserstein (FUGW). The method aligns cortical surfaces based on the similarity of their functional signatures in response to a variety of stimulation settings, while penalizing large deformations of individual topographic organization. We demonstrate that FUGW is well-suited for whole-brain landmark-free alignment. The unbalanced feature allows to deal with the fact that functional areas vary in size across subjects. Our results show that FUGW alignment significantly increases between-subject correlation of activity for independent functional data, and leads to more precise mapping at the group level.
Add the full text or supplementary notes for the publication here using Markdown formatting.